Mediation
Mediation
In statistics, a mediation model is one that seeks to identify and explain the mechanism or process that underlies an observed relationship between an independent variable and a dependent variable via the inclusion of a third hypothetical variable, known as a mediator variable (also a mediating variable, intermediary variable, or intervening variable) (Wikipedia, 2024).
Causality
Mediation does not imply causation!
All requirements need to be met:
- Correlation
- Time order
- No spurious (false) correlation
- No common cause confounder
Example
Does the speed of recovery after sickness improve with the use of alternative medicine or is this effect mediated by a healthy lifestyle?
Mediaton paths
The data
Apply 3 models
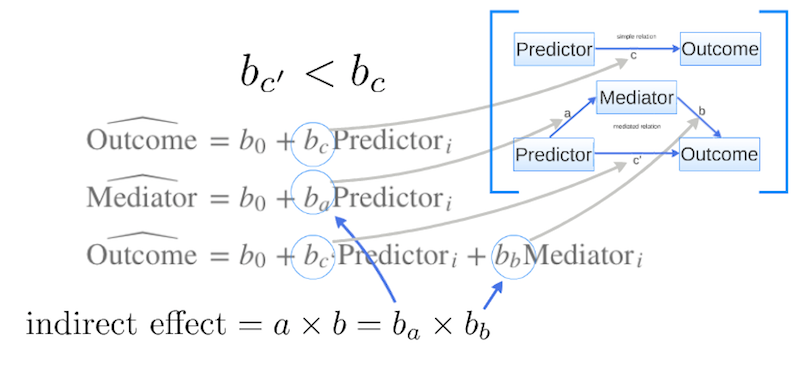
\[\widehat{\text{Outcome}} = b_0 + b_c \times \text{Predictor}_i\]
| Dependent variable | |||
| Predictors | Estimates | CI | p |
| (Intercept) | 12.48 | 9.71 – 15.24 | <0.001 |
| use homeopathic remedies | 4.76 | 4.48 – 5.04 | <0.001 |
| Observations | 100 | ||
| R2 / R2 adjusted | 0.922 / 0.921 | ||
\[\widehat{\text{Mediator}} = b_0 + b_a \times \text{Predictor}_i\]
| Dependent variable | |||
| Predictors | Estimates | CI | p |
| (Intercept) | 1.87 | 1.12 – 2.61 | <0.001 |
| use homeopathic remedies | 1.21 | 1.14 – 1.29 | <0.001 |
| Observations | 100 | ||
| R2 / R2 adjusted | 0.913 / 0.912 | ||
\[\widehat{\text{Outcome}} = b_0 + b_{c`} \times \text{Predictor}_i + b_b \times \text{Mediator}_i\]
| Dependent variable | |||
| Predictors | Estimates | CI | p |
| (Intercept) | 7.14 | 5.15 – 9.12 | <0.001 |
| use homeopathic remedies | 1.30 | 0.70 – 1.91 | <0.001 |
| healthy lifestyle | 2.86 | 2.38 – 3.34 | <0.001 |
| Observations | 100 | ||
| R2 / R2 adjusted | 0.968 / 0.968 | ||
Extract beta coëfficients
\[ \begin{aligned} b_a &= 1.21 \\ b_b &= 2.86 \\ b_c &= 4.762 \\ b_{c`} &= 1.301 \\ \end{aligned} \]
Path model
Visual
3D Visual
Interactive, give it a spin.
Indirect effect
\(a \times b = b_a \times b_b\)
b.a*b.buse.homeopathic.remedies
3.461192 b.c - b.c.accentuse.homeopathic.remedies
3.461192 Indirect effect (partially standardized)
\(\frac{ab}{s_{Outcome}} = \frac{b_a b_b}{s_{Outcome}}\)
b.a*b.b/sd(speed.of.healing)use.homeopathic.remedies
0.3833868 Indirect effect (standardized)
\(\frac{ab}{s_{Outcome}} \times s_{Predictor} = \frac{b_a b_b}{s_{Outcome}} \times s_{Predictor}\)
b.a*b.b/sd(speed.of.healing)*sd(use.homeopathic.remedies)use.homeopathic.remedies
0.6979258 Types of mediation
- Parallel mediation
- Serial mediation
- Combined serial and parallel mediation
- Mediation with covariates
- Combined mediation and moderation

