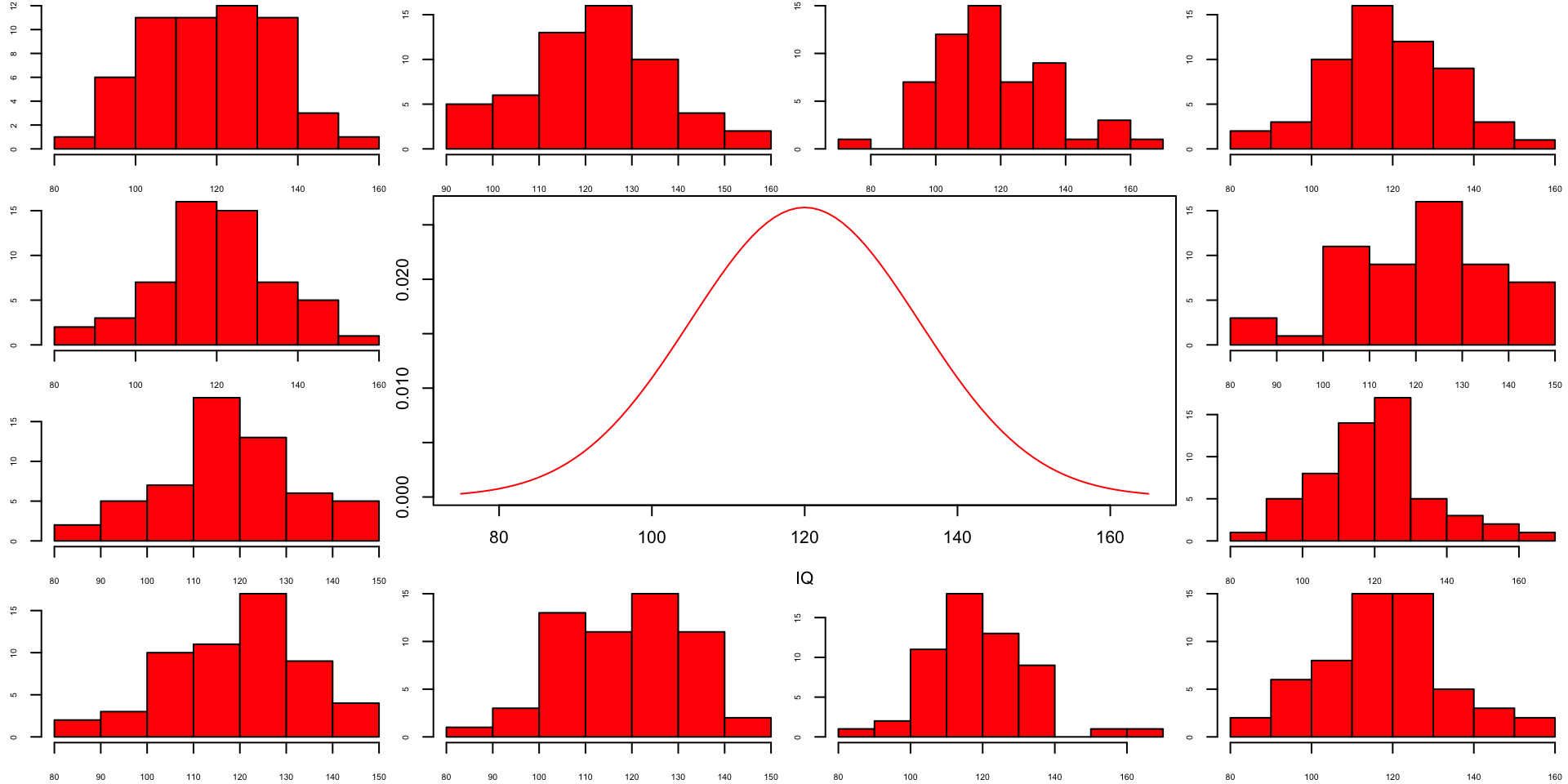
layout(matrix(c(2:6,1,1,7:8,1,1,9:13), 4, 4))
n = 56 # Sample size
df = n - 1 # Degrees of freedom
mu = 120
sigma = 15
IQ = seq(mu-45, mu+45, 1)
par(mar=c(4,2,0,0))
plot(IQ, dnorm(IQ, mean = mu, sd = sigma), type='l', col="red")
n.samples = 12
for(i in 1:n.samples) {
par(mar=c(2,2,0,0))
hist(rnorm(n, mu, sigma), main="", cex.axis=.5, col="red")
}F-Distribution and factorial ANOVA
University of Amsterdam
2024-09-30
F-distribution
Ronald Fisher
The F-distribution, also known as Snedecor’s F distribution or the Fisher–Snedecor distribution (after Ronald Fisher and George W. Snedecor) is, in probability theory and statistics, a continuous probability distribution. The F-distribution arises frequently as the null distribution of a test statistic, most notably in the analysis of variance; see F-test.
Sir Ronald Aylmer Fisher FRS (17 February 1890 – 29 July 1962), known as R.A. Fisher, was an English statistician, evolutionary biologist, mathematician, geneticist, and eugenicist. Fisher is known as one of the three principal founders of population genetics, creating a mathematical and statistical basis for biology and uniting natural selection with Mendelian genetics.
Analysing variance
Decomposing variance example of height for males and females.
Population distribution
Population distribution
F-statistic
\(F = \frac{{MS}_{model}}{{MS}_{error}} = \frac{\text{between group var.}}{\text{within group var.}} = \frac{Explained}{Unexplained} = \frac{{SIGNAL}}{{NOISE}}\)
The \(F\)-statistic represents a signal to noise ratio by defiding the model variance component by the error variance component.
A samples
Let’s take two sample from our normal population and calculate the F-value.
\[F = \frac{{MS}_{model}}{{MS}_{error}} = \frac{{SIGNAL}}{{NOISE}} = \frac{{522.11}}{{296.77}} = 1.76\]
More samples
let’s take more samples and calculate the F-value every time.
n.samples = 1000
f.values = vector()
for(i in 1:n.samples) {
x.1 = rnorm(n, mu, sigma); x.1
x.2 = rnorm(n, mu, sigma); x.2
data <- data.frame(group = rep(c("s1", "s2"), each=n), score = c(x.1,x.2))
f.values[i] = summary(aov(lm(score ~ group, data)))[[1]]$F[1]
}
k = 2
N = 2*n
df.model = k - 1
df.error = N - k
hist(f.values, freq = FALSE, main="F-values", breaks=100)
F = seq(0, 6, .01)
lines(F, df(F,df.model, df.error), col = "red")More samples
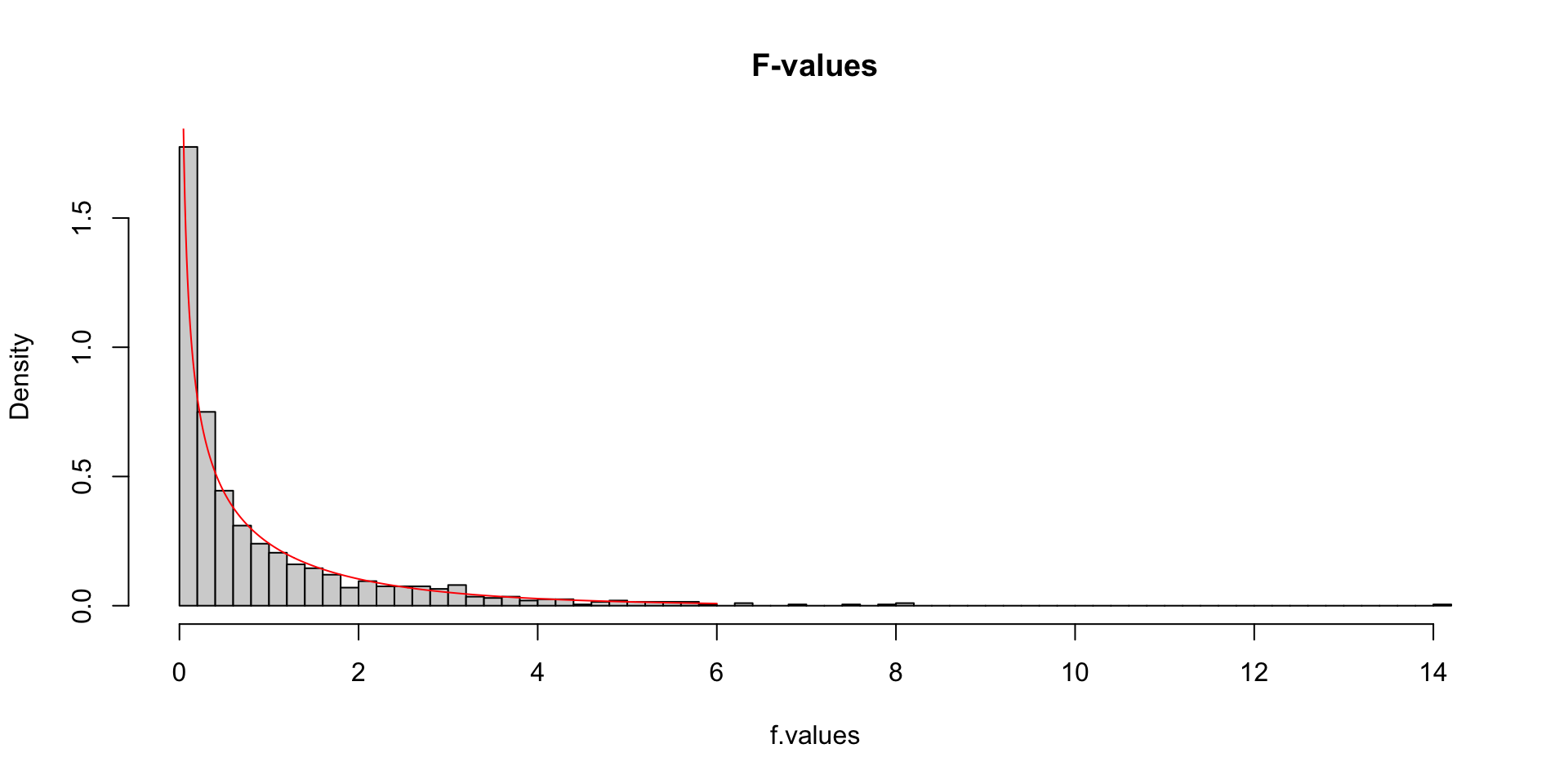
F-distribution
So if the population is normally distributed (assumption of normality) the f-distribution represents the signal to noise ratio given a certain number of samples (\({df}_{model} = k - 1\)) and sample size (\({df}_{error} = N - k\)).
The F-distibution therefore is different for different sample sizes and number of groups.
\[\frac{\sqrt{\frac{(d_1x)^{d_1}\,\,d_2^{d_2}} {(d_1x+d_2)^{d_1+d_2}}}} {x\operatorname{B}\left(\frac{d_1}{2},\frac{d_2}{2}\right)}\]
Warning
Formula not exam material
F-distribution
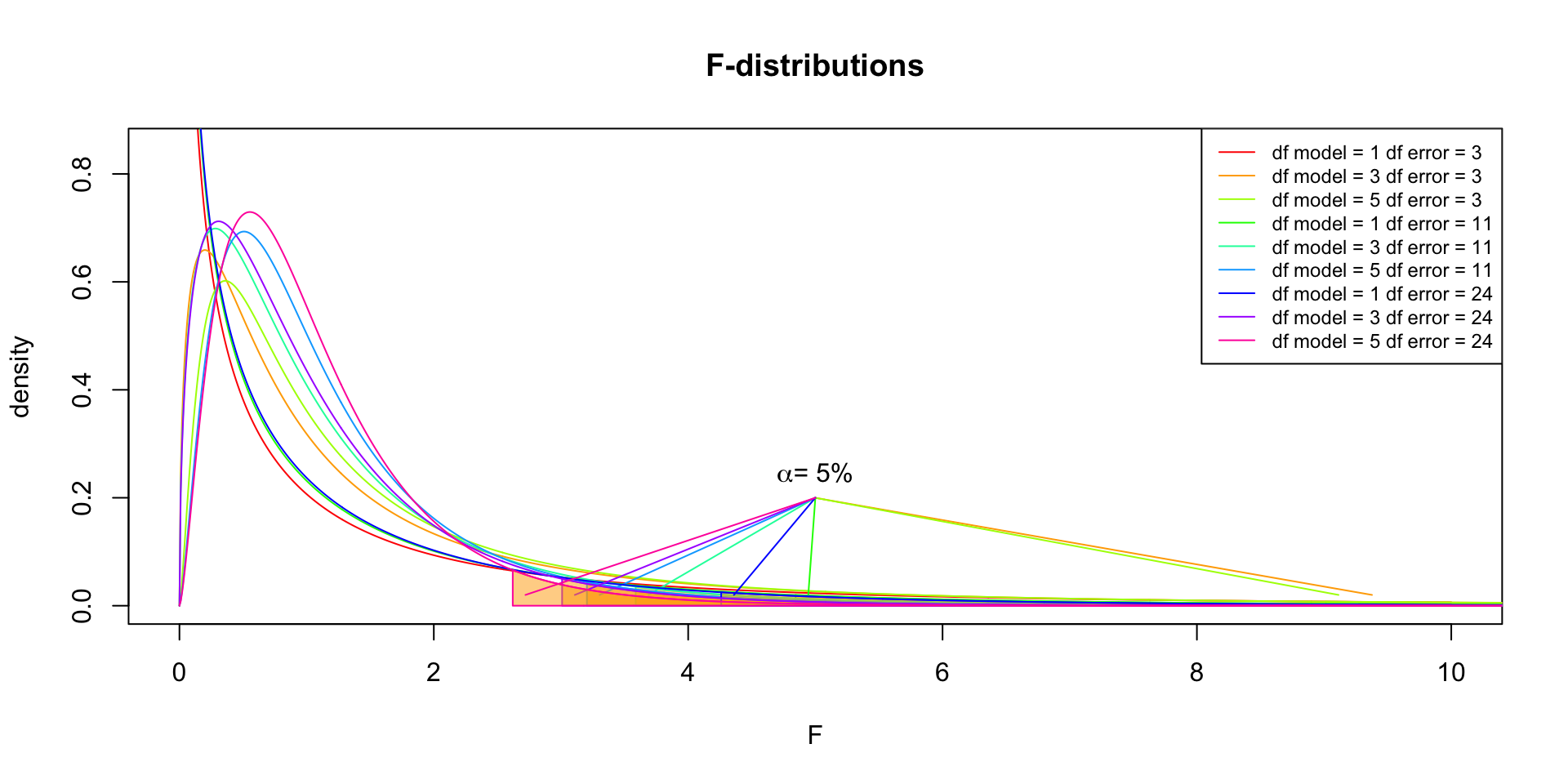
F-distribution
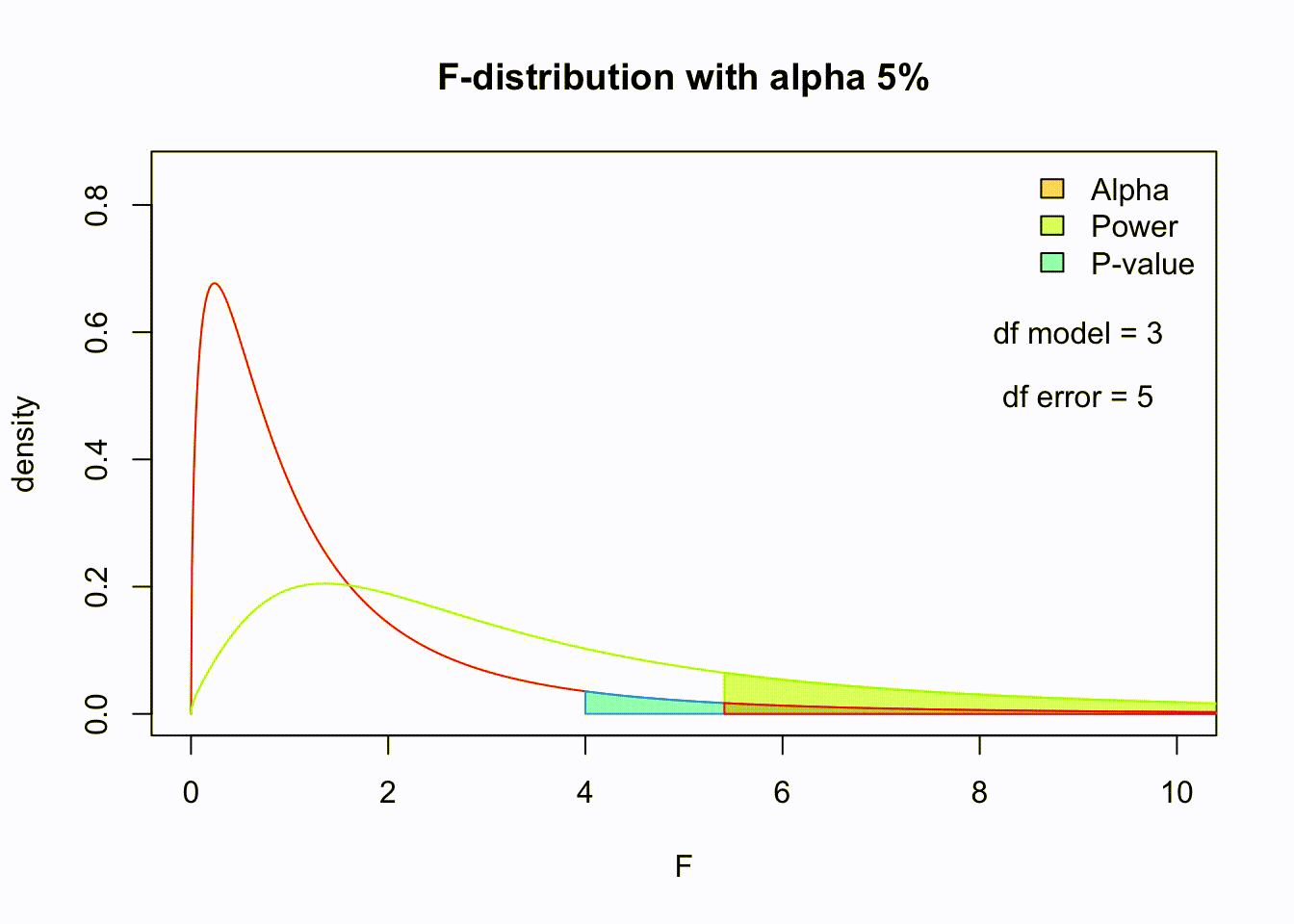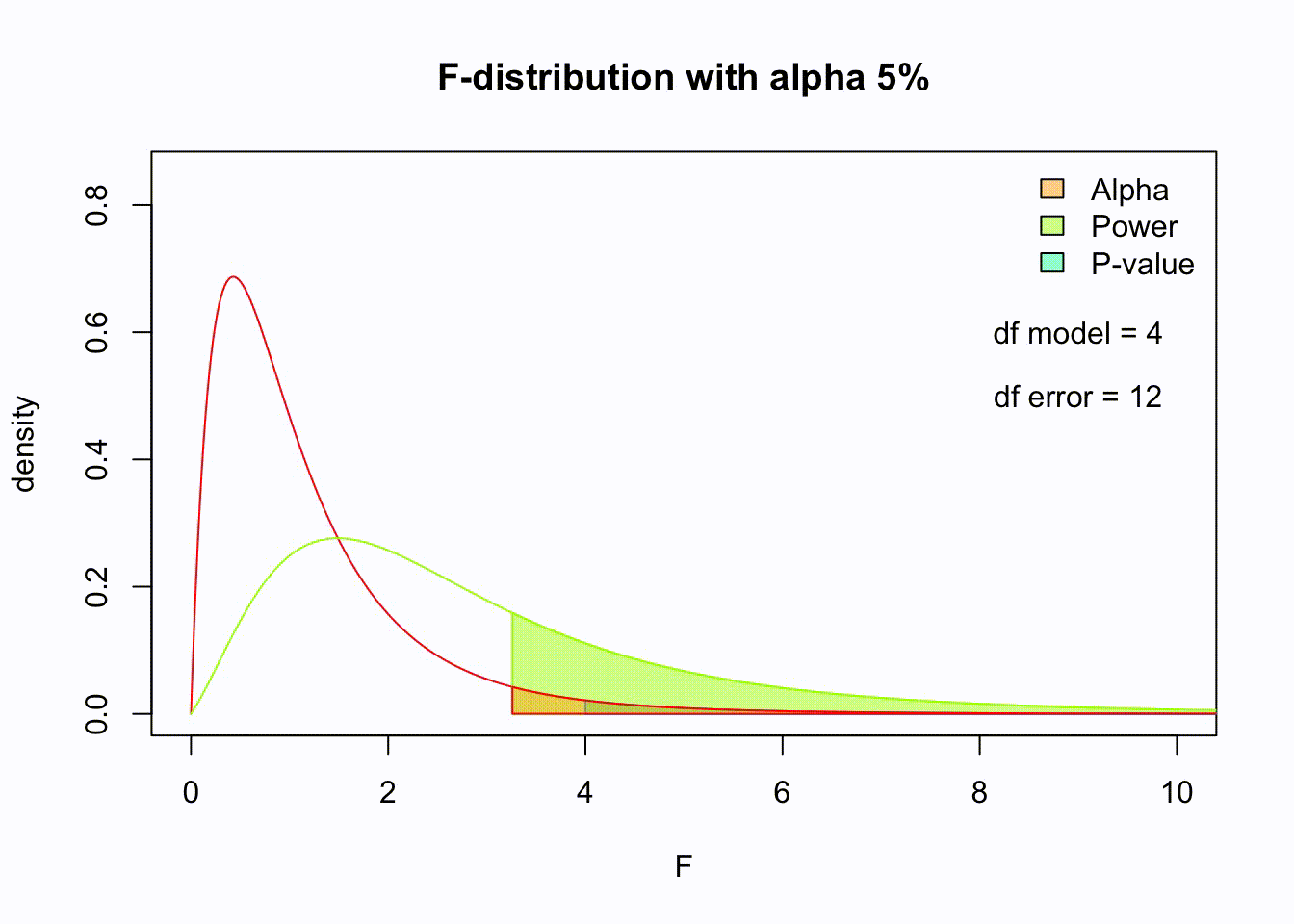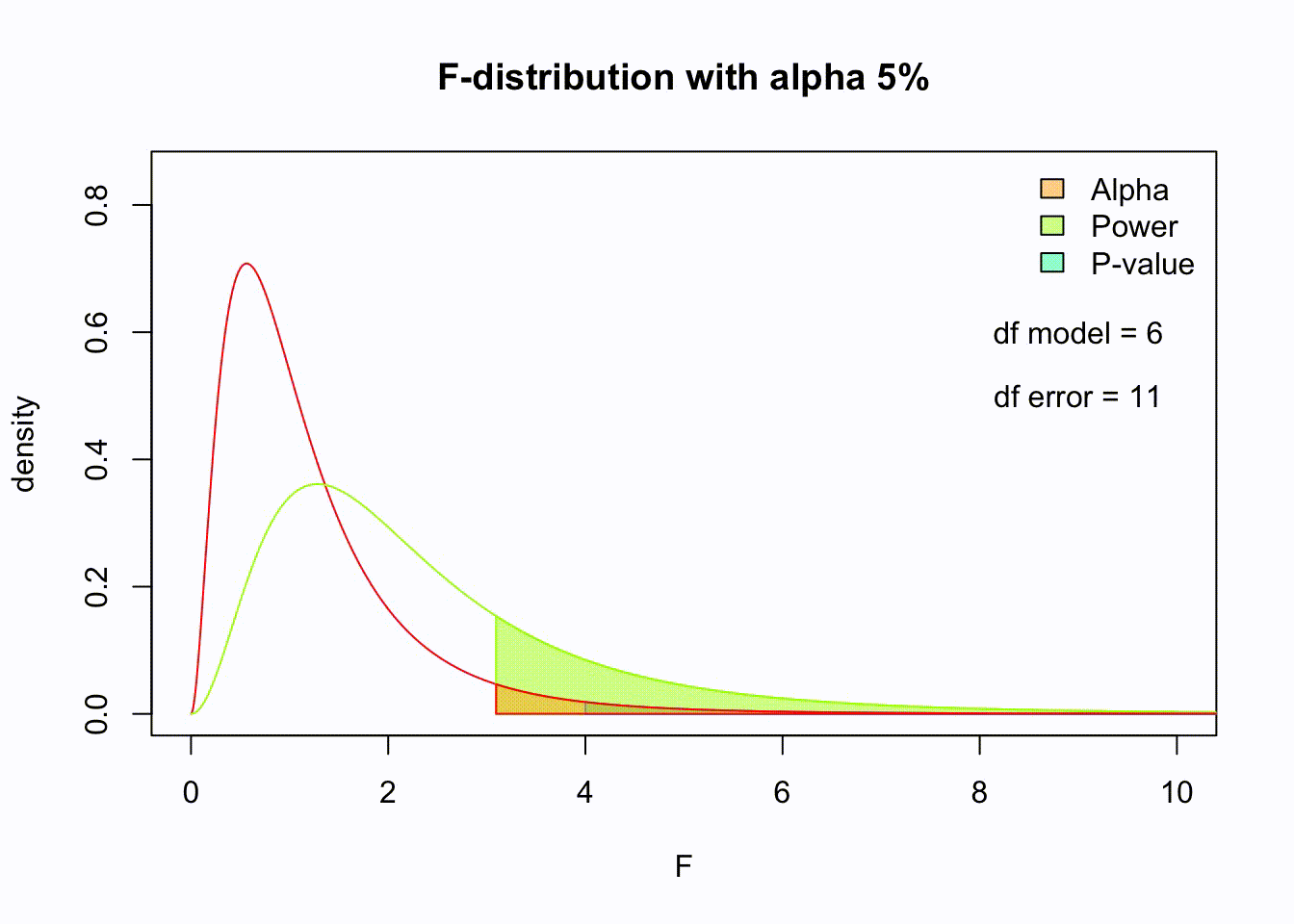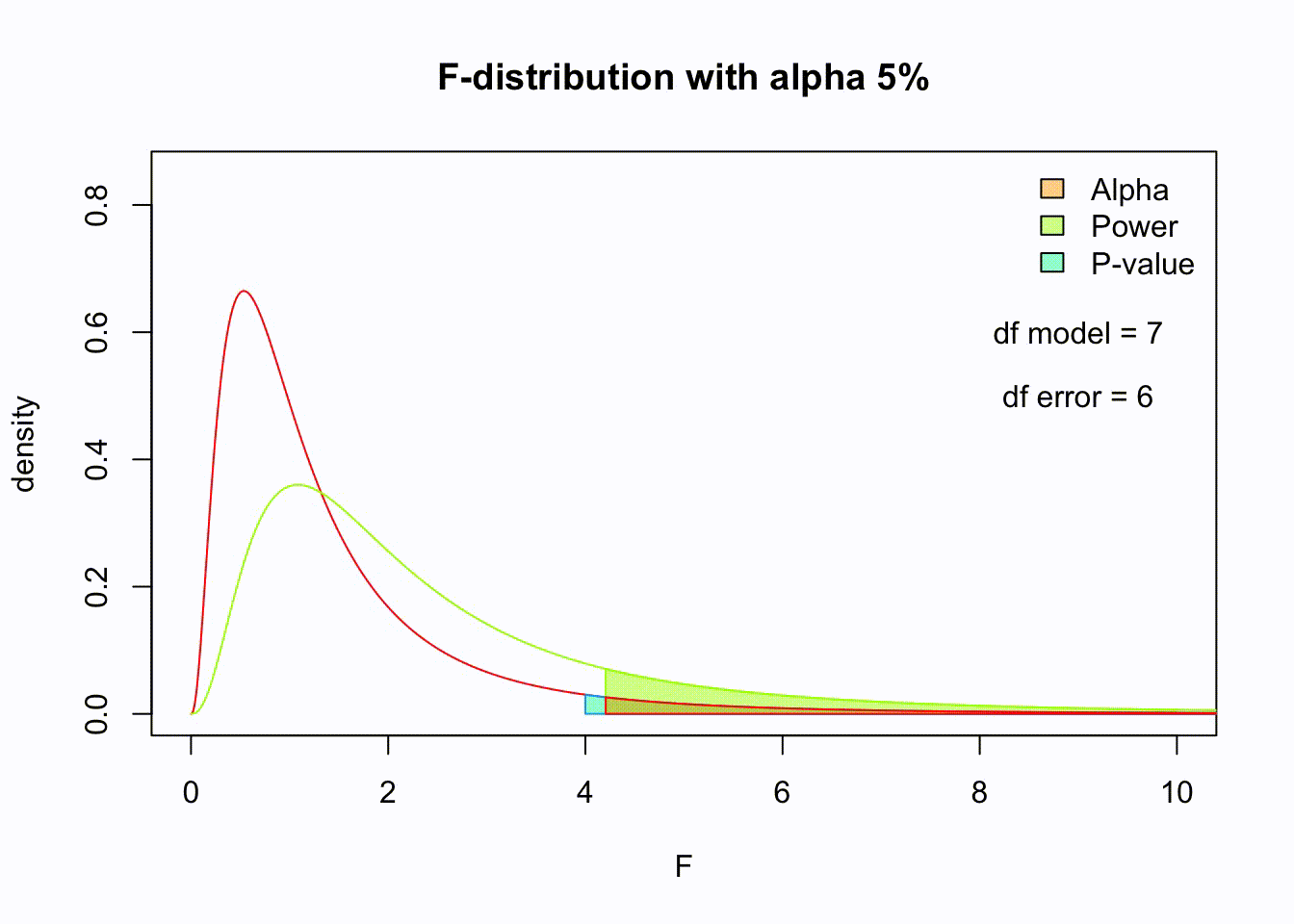
Animated F-distrigutions
Independent factorial ANOVA
Two or more independent variables with two or more categories. One dependent variable.
Independent factorial ANOVA
The independent factorial ANOVA analyses the variance of multiple independent variables (Factors) with two or more categories.
Effects and interactions/moderation:
- 1 dependent/outcome variable
- 2 or more independent/predictor variables
- 2 or more cat./levels
Flow chart
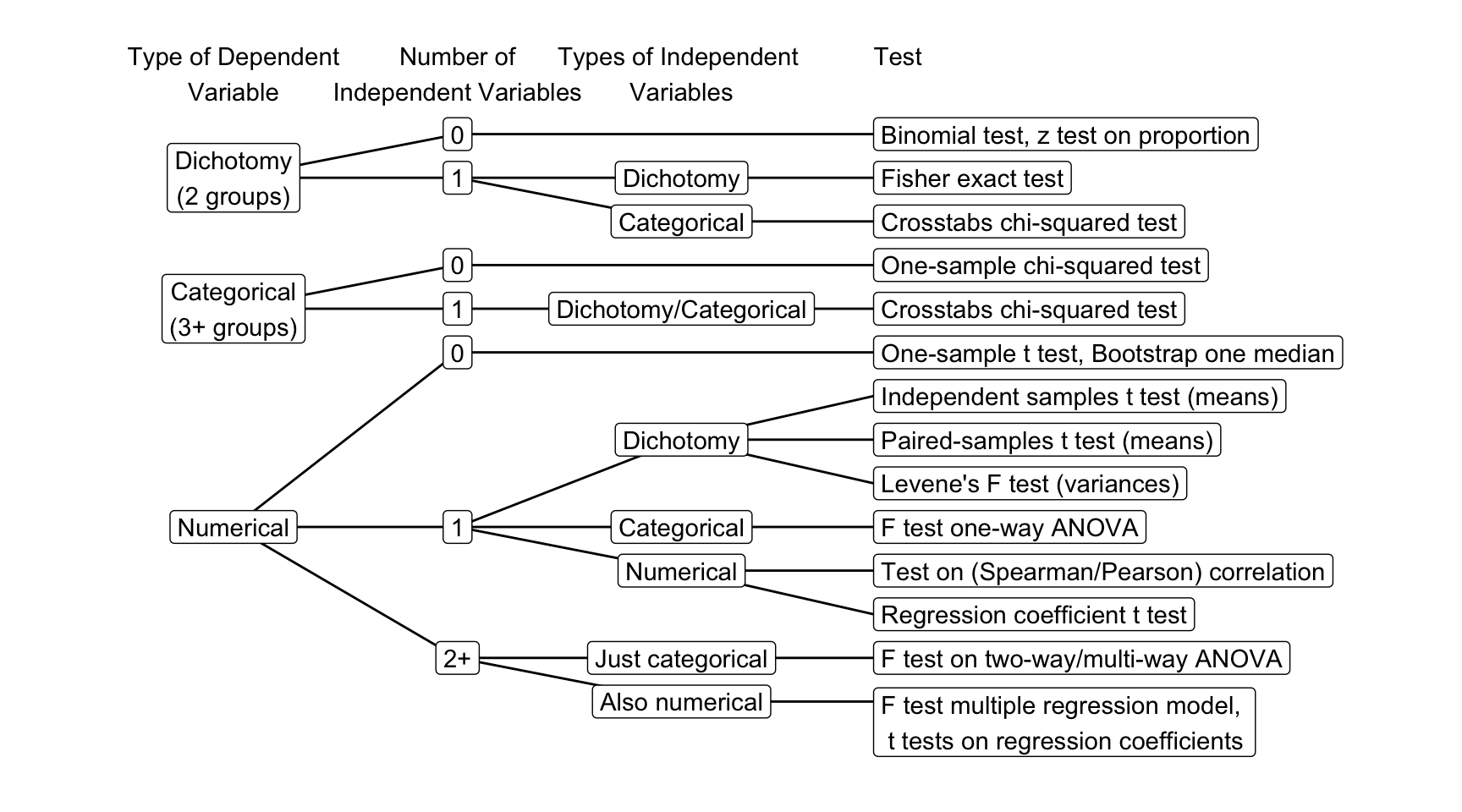
Flow chart statistical test selection
Assumptions
- Continuous variable
- Random sample
- Normaly distributed
- Shapiro-Wilk test
- Equal variance within groups
- Levene’s test
Example
In this example we will look at the amount of accidents in a car driving simulator while subjects where given varying doses of speed and alcohol.
- Dependent variable
- Accidents
- Independent variables
- Speed
- None
- Small
- Large
- Alcohol
- None
- Small
- Large
- Speed
| person | alcohol | speed | accidents |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 |
| 2 | 1 | 2 | 2 |
| 3 | 1 | 3 | 4 |
| 4 | 2 | 1 | 6 |
| 5 | 2 | 2 | 8 |
| 6 | 2 | 3 | 10 |
| 7 | 3 | 1 | 12 |
| 8 | 3 | 2 | 14 |
| 9 | 3 | 3 | 16 |
Data
Effects
- Total
- \(F = \frac{{MS}_{model}}{{MS}_{error}}\)
- Main effects
- \(F = \frac{{MS}_{goup A}}{{MS}_{error}}\)
- \(F = \frac{{MS}_{goup B}}{{MS}_{error}}\)
- Interaction/moderation
- \(F = \frac{{MS}_{A \times B}}{{MS}_{error}}\)
\(MS = \text{Mean Squares}\)
\(MS = \frac{SS}{df}\)
\(SS = \text{Sums of Squares}\)
\(df = \text{degrees of freedom}\)
SS model
\(\text{SS}_\text{model} = 494.22048\)
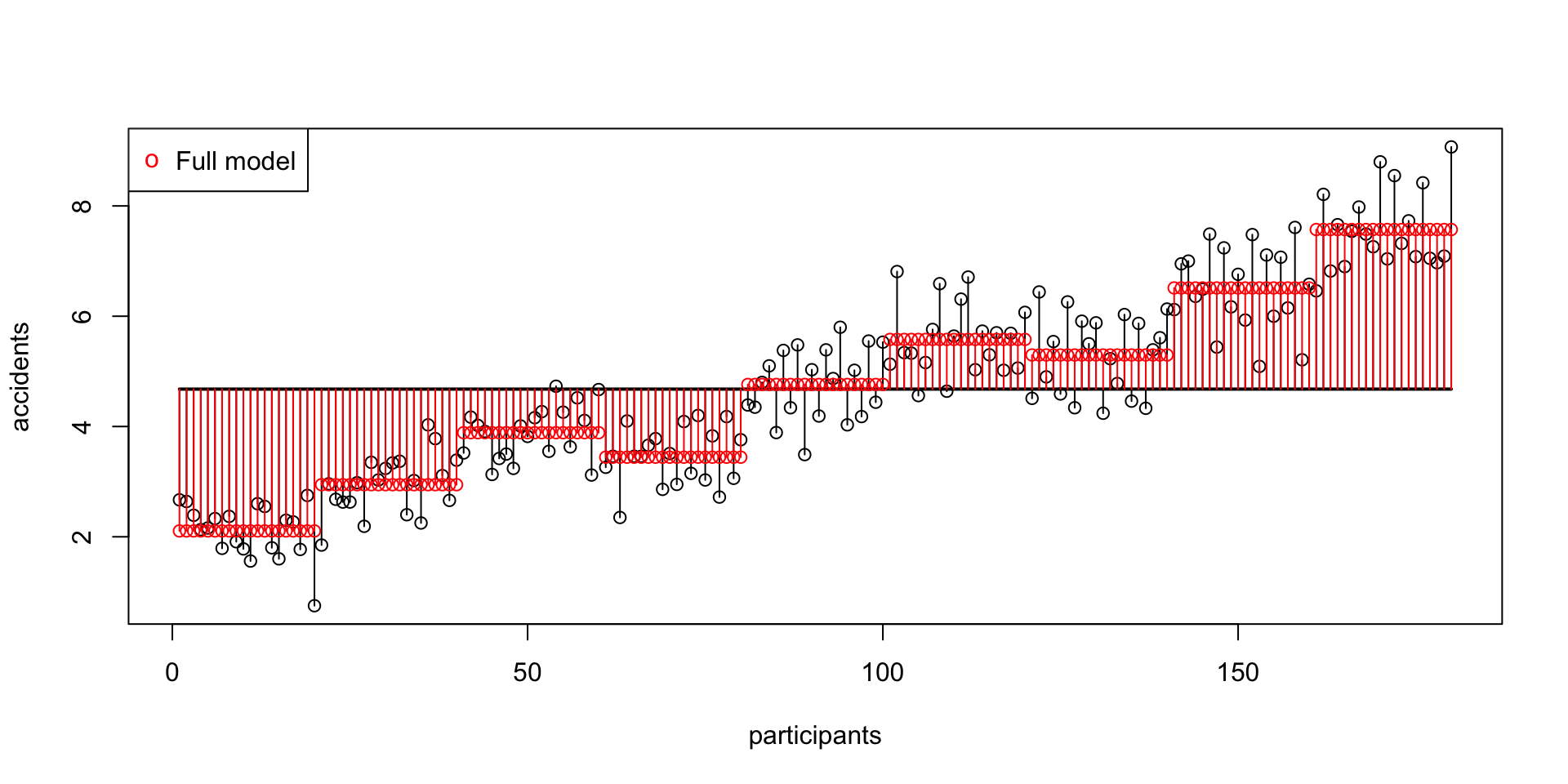
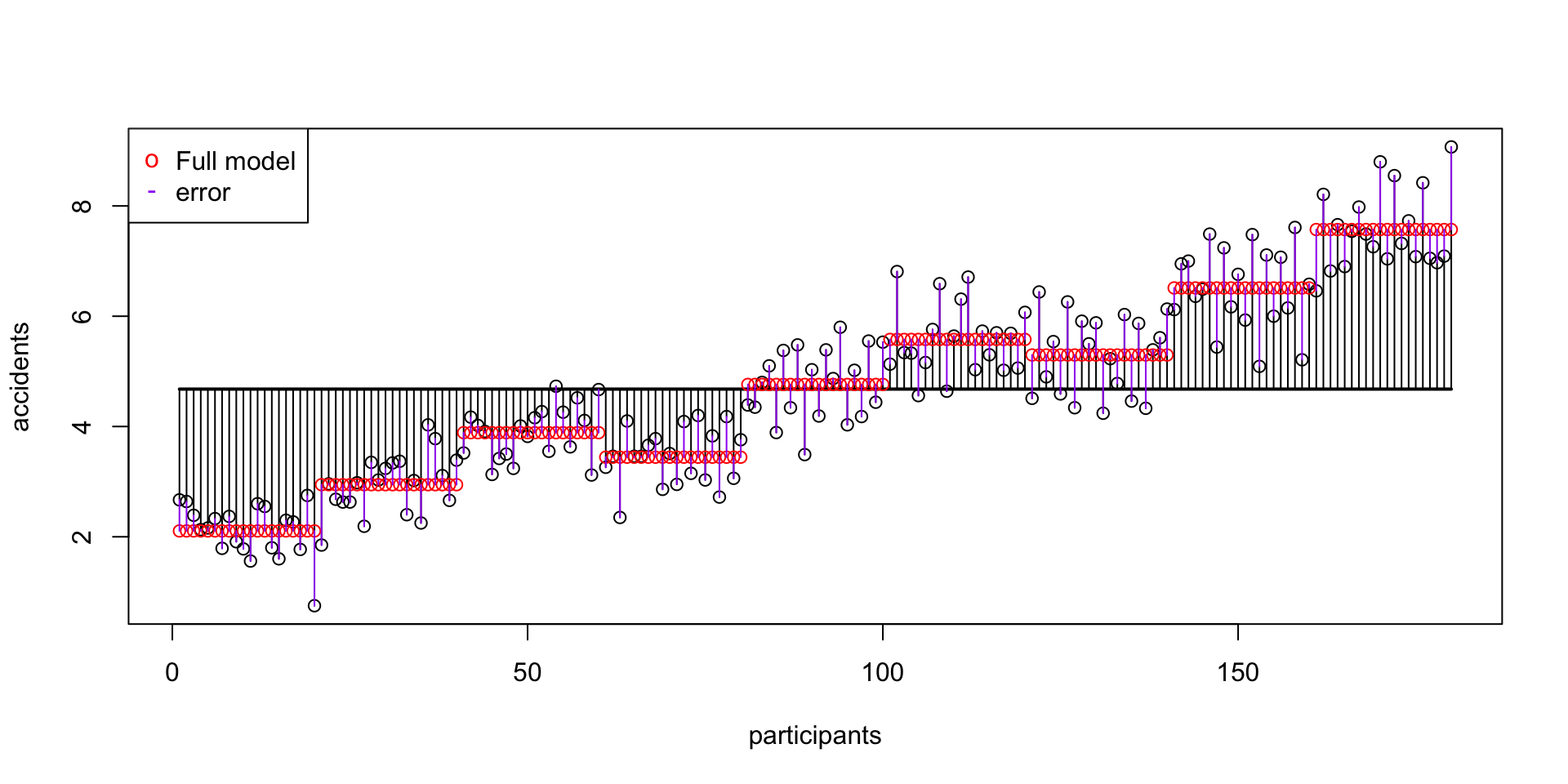
SS error
\(\text{SS}_\text{error} = 66.34642\)
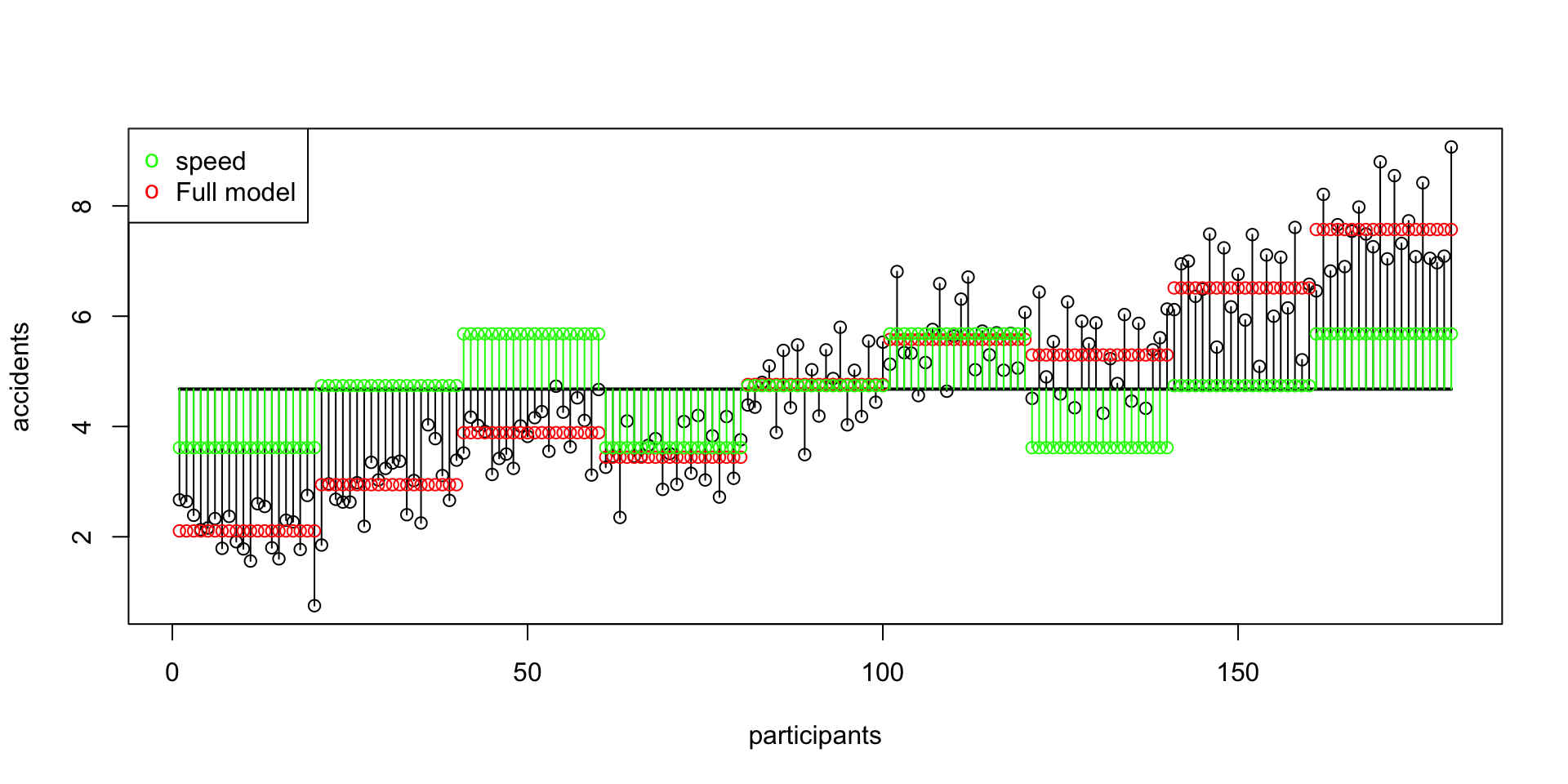
SS A Speed
\(\text{SS}_\text{speed} = 128.1639233\)
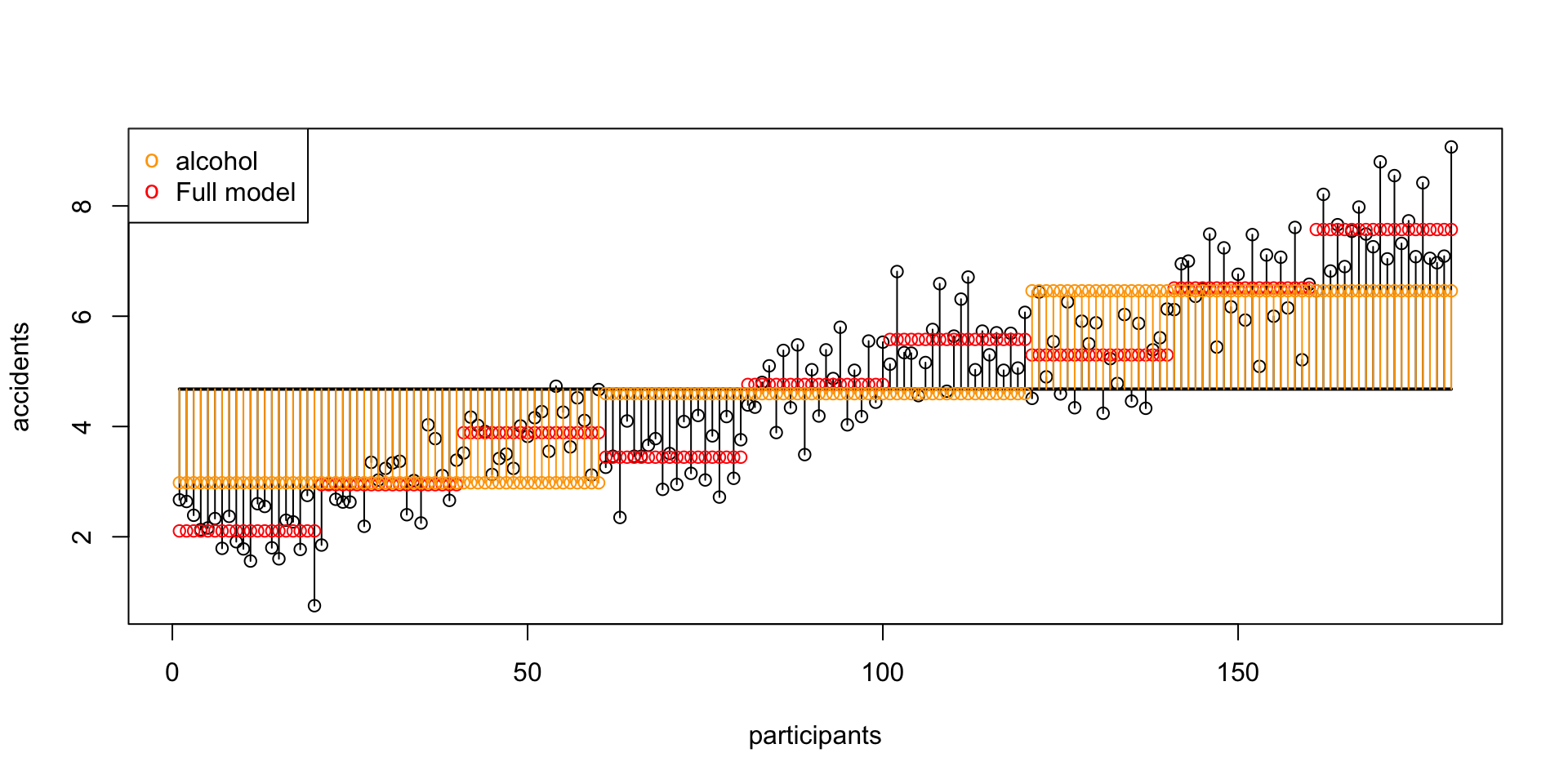
SS B Alcohol
\(\text{SS}_\text{alcohol} = 364.14583\)
SS AB Alcohol x Speed
| Variance | Sum of squares | df | Mean squares | F-ratio |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| \(\hspace{2ex}AB\) | \(\text{SS}_{A \times B} = \text{SS}_{\text{model}} - \text{SS}_{\text{A}} - \text{SS}_{\text{B}}\) | \(df_A \times df_B\) | \(\frac{\text{SS}_{\text{AB}}}{\text{df}_{\text{AB}}}\) | \(\frac{\text{MS}_{\text{AB}}}{\text{MS}_{\text{error}}}\) |
\[\text{SS}_{\text{speed} \times \text{alcohol}} = 1.9107267\]
Mean Squares
Mean squares for:
- Speed
- Alcohol
- Speed \(\times\) Alcohol
\[\begin{aligned} F_{Speed} &= \frac{{MS}_{Speed}}{{MS}_{error}} \\ F_{Alcohol} &= \frac{{MS}_{Alcohol}}{{MS}_{error}} \\ F_{Alcohol \times Speed} &= \frac{{MS}_{Alcohol \times Speed}}{{MS}_{error}} \\ \end{aligned}\]
Interaction
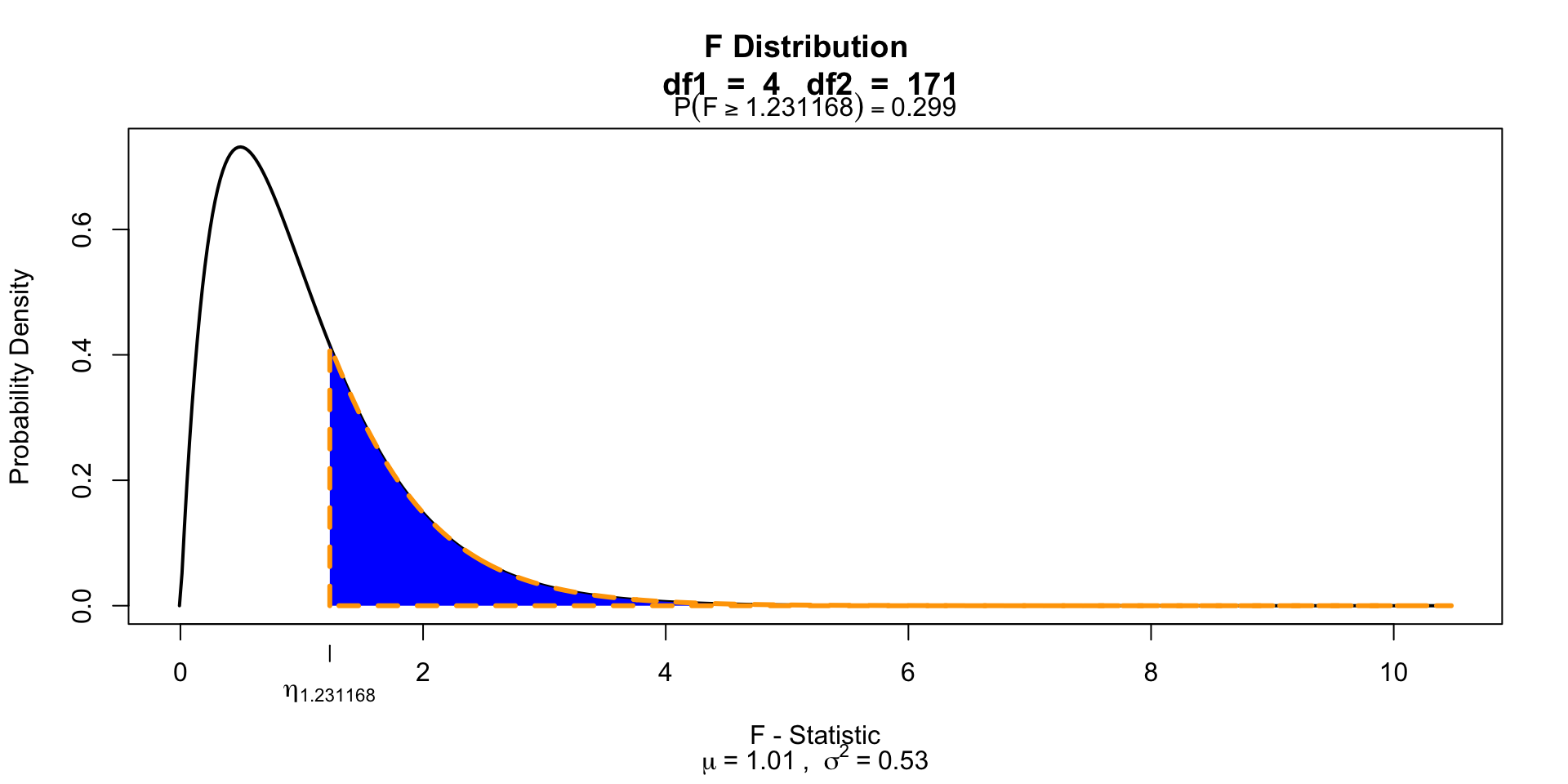
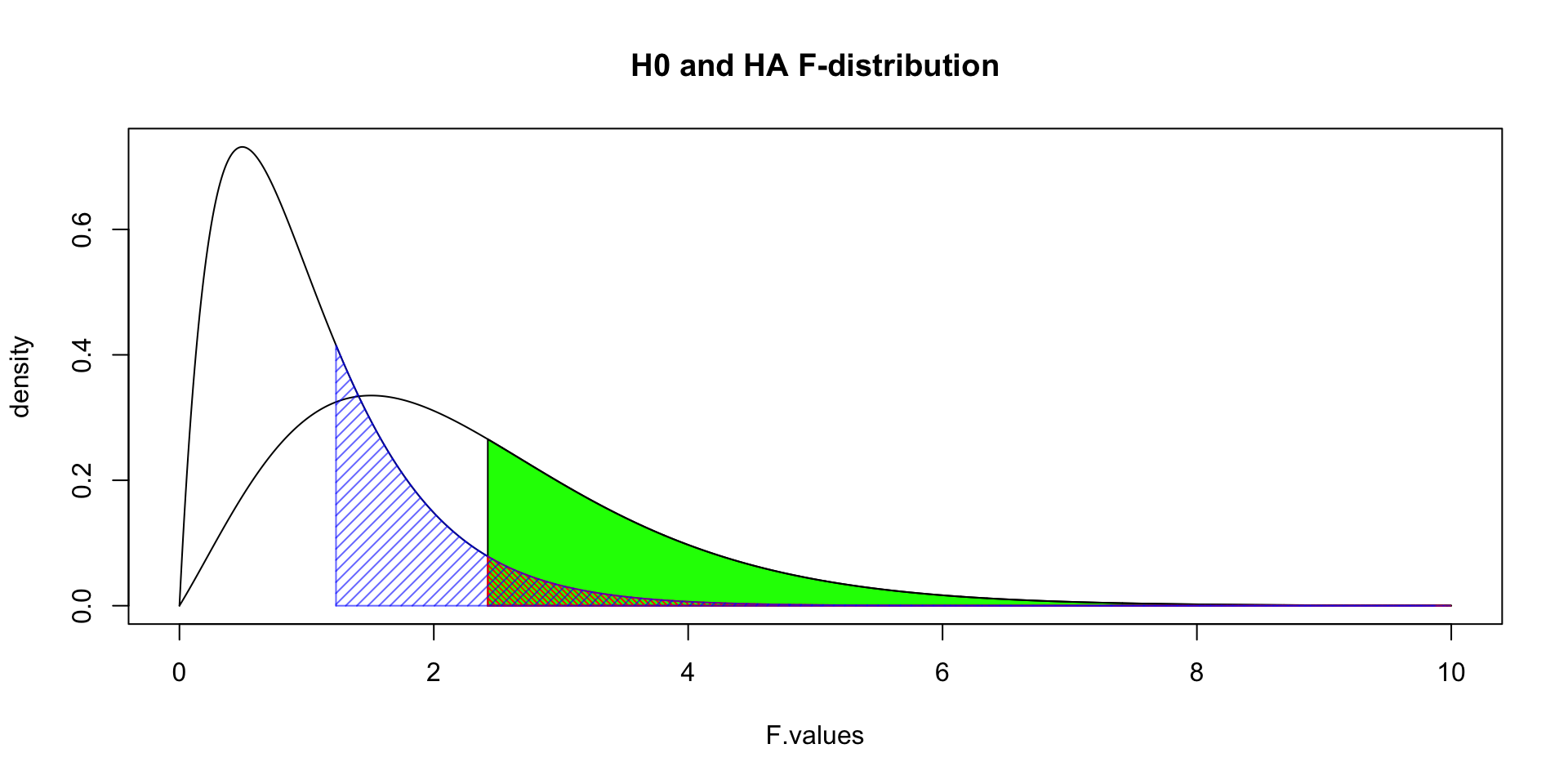
\[F_{Alcohol \times Speed} = \frac{{MS}_{Alcohol \times Speed}}{{MS}_{error}} = \frac{0.48}{0.39} = 1.23\]
\(P\)-value
Post-Hoc
Unplanned comparisons
- Exploring all possible differences
- Adjust T value for inflated type 1 error
Effect size
General effect size measures
- Amount of explained variance \(R^2\) also called eta squared \(\eta^2\).
Effect sizes of post-hoc comparisons
- Cohen’s \(r\) gives the effect size for a specific comparison
- \(r_{Contrast} = \sqrt{\frac{t^2}{t^2+{df}}}\)
End
Contact

Statistical Reasoning 2024-2025
